Where Are the Sierra Nevada?
The Sierra Nevada is a mountain range that is situated in the Western part of the United States. They are primarily located along the eastern part of California.
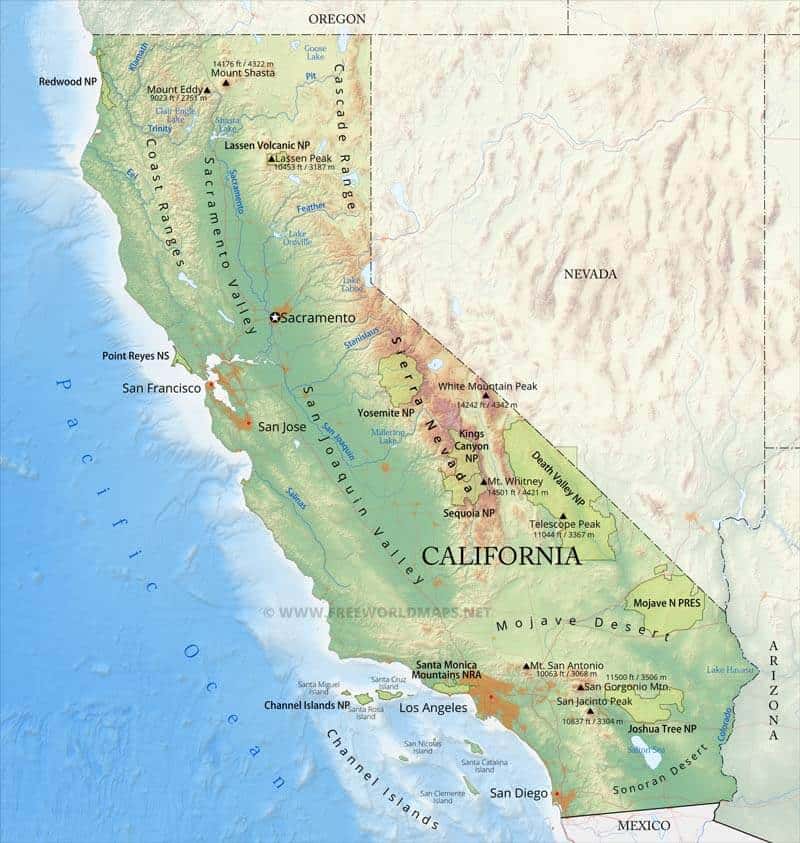
How Long Are the Sierra Nevada?
The Sierras are approximately 400 miles (640 kilometers) long from north to south and between 50 to 80 miles (80-130 kilometers) wide from east to west.
How Big and Tall Are the Mountains in the Sierra Nevada?
The Sierra Nevada encompass a wide range of elevations, with Mount Whitney standing as its highest peak at 14,505 feet (4,421 meters) above sea level. Mount Whitney is the tallest peak in the contiguous United States. The highest peak in the United States is Denali (20,310 feet / 6,190 meters), which located in Alaska. Denali is also the highest peak in North America, making it is one of the seven summits.

What States Are the Sierra Nevada In?
The Sierra Nevada are located mostly within the state of California, though a portion known as the Carson Range spur spills into Nevada.
What Does Sierra Nevada Mean?
Sierra Nevada means “snow-covered mountain range” in Spanish.
Is It “Sierra” or “Sierras?”
The Sierra Nevada are commonly referred to as the Sierra or Sierras. Because the word “Sierra” is already plural in its root language, some argue that calling the mountain range the “Sierras” is grammatically incorrect because it would be redundant to pluralize Sierra with an ‘s.’ However, others justify the use of “Sierras” because it is a nickname, similar to the Rockies (for the Rocky Mountains) and the Smokies (for the Smoky Mountains). In other words, both Sierra or Sierras are considered OK.

Where Do the Sierra Nevada Mountains Start and End?
The Sierra Nevada range begins in the vicinity of the Susan River in northern California and extends southward to the Tehachapi Pass in Kern County, showcasing an array of stunning peaks, valleys, and natural features along its course.
How Did the Sierra Nevada Mountains Form?
The formation of the Sierra Nevada mountain range is attributed to the movement of tectonic plates. Around 100 million years ago during the Mesozoic Era, the Farallon Plate began to slide beneath the North American Plate.

This caused magma to rise from the Earth’s mantle beneath the western edge of North America. The magma gradually cooled and solidified below the surface, forming an granitic intrusion known as the Sierra Nevada Batholith.
Around 5 to 3 million years ago during the Cenozoic Era, intense faulting and uplifting occurred, further shaping and elevating the Sierra Nevada. This tectonic activity resulted in the rise of the prominent peaks, valleys, and steep slopes characteristic of the range. The Sierras are folded mountains.
Are the Sierra Nevada Mountains Part of the Rocky Mountains?
No, the Sierra Nevada Mountains are not part of the Rocky Mountains. They are situated farther west and are separate from the Rockies.
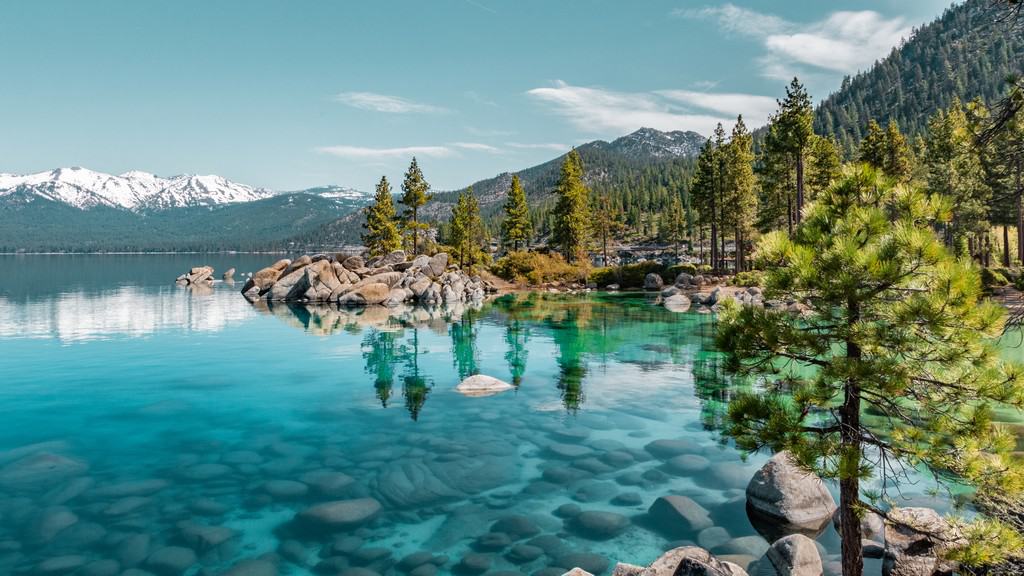
What are the Most Famous Destinations in the Sierra Nevada?
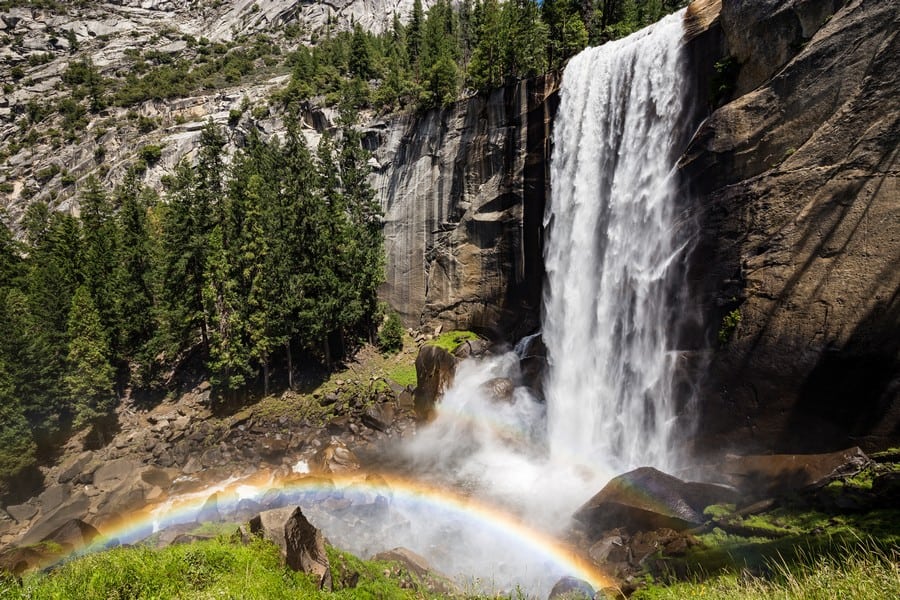

The Sierra Nevada Mountains are renowned for a multitude of natural landmarks:
- Yosemite National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most iconic national parks in the United States, Yosemite is famous for its towering granite cliffs, breathtaking waterfalls like Yosemite Falls and Bridalveil Fall, giant sequoias in Mariposa Grove, and the scenic Yosemite Valley.
- Lake Tahoe: Straddling the border between California and Nevada, Lake Tahoe is a pristine alpine lake known for its crystal-clear waters, surrounded by picturesque mountains. It offers year-round recreational activities such as skiing, snowboarding, hiking, boating, and beach relaxation.
- Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks: These two parks, often managed together, are home to some of the world’s largest trees, including General Sherman, the largest tree on Earth by volume. Visitors can explore impressive groves of giant sequoias, deep canyons, and rugged wilderness.
- Mammoth Lakes: A popular resort town located near Mammoth Mountain, offering skiing and snowboarding in the winter and hiking, mountain biking, and fishing during the warmer months. The area also features natural hot springs and stunning alpine lakes.
- Mono Lake: Known for its unique tufa towers and saline waters, Mono Lake is a fascinating destination for birdwatching and photography. It provides a glimpse into unusual geological formations and diverse ecosystems.
- Devils Postpile National Monument: This geological wonder consists of basalt columns formed from lava flows thousands of years ago. The monument also features Rainbow Falls and offers hiking opportunities in a pristine setting.
- Ansel Adams Wilderness: Named after the renowned landscape photographer, this wilderness area within the Sierra Nevada offers stunning scenery, alpine lakes, and opportunities for backpacking, fishing, and solitude.
What are Some Notable Peaks in the Sierra Nevada?
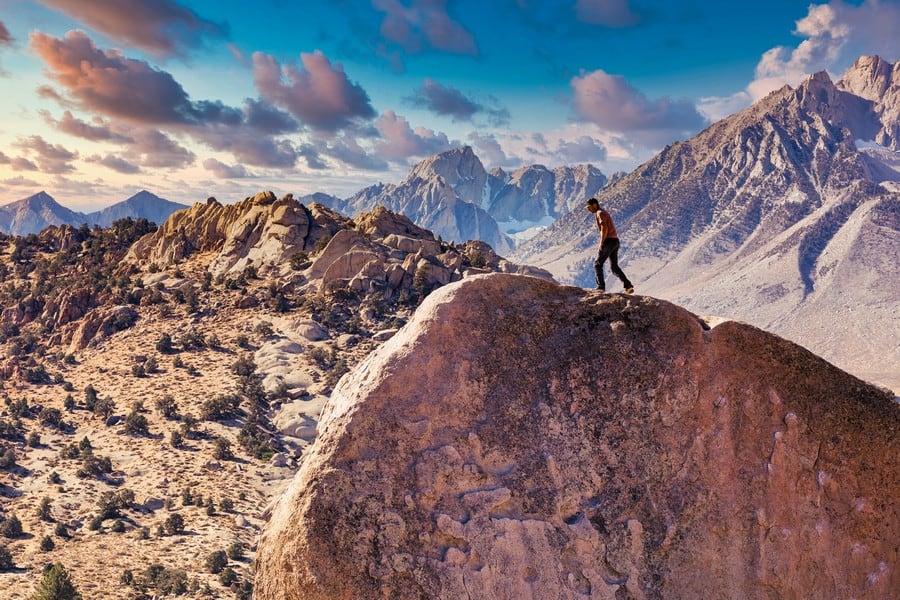

These are the notable peaks in the Sierras:
- Mount Whitney: The highest point in the Sierra Nevada and the contiguous United States, Mount Whitney is 14,505 feet (4,421 meters) tall.
- Mount Williamson: This peak, with an elevation of 14,379 feet (4,383 meters), is among the highest in the Sierra Nevada and offers stunning views.
- North Palisade: Known for its challenging climbing routes, North Palisade reaches an elevation of 14,248 feet (4,343 meters),.
- Mount Russell: Standing at 14,094 feet (4,296 meters), Mount Russell is another prominent peak and is admired by climbers for its technical routes.
- Split Mountain: With an elevation of 14,058 feet (4,285 meters), Split Mountain is a picturesque peak.
- Mount Langley: At 14,026 feet (4,276 meters), Mount Langley is a popular destination for hikers.
What are Some Notable Hikes in the Sierra Nevada?
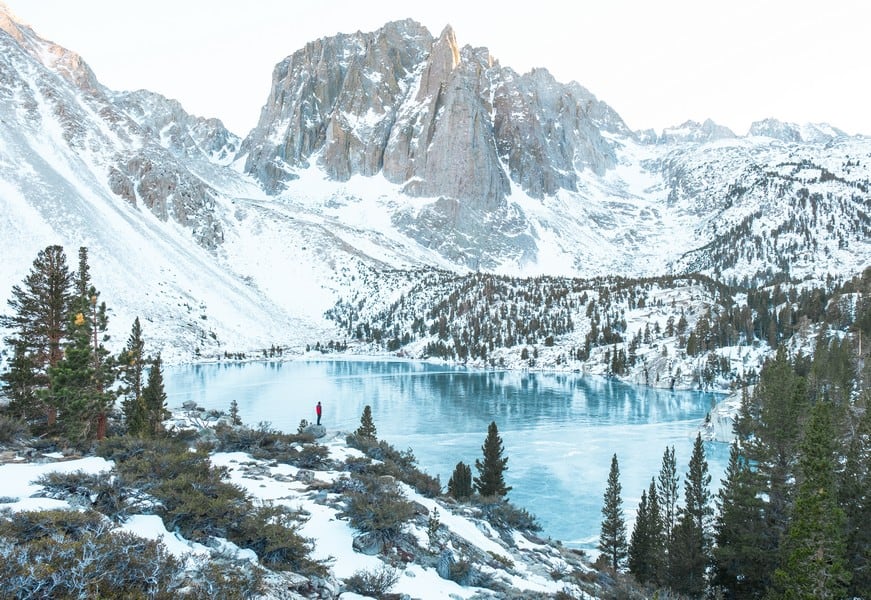

The Sierra Nevada mountain range offers a variety of trails:
- John Muir Trail (JMT): One of the most famous long-distance trails in the world, the John Muir Trail spans approximately 211 miles, starting from Yosemite Valley in Yosemite National Park and ending at the summit of Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the contiguous United States. The trail traverses through remarkable alpine scenery, mountain passes, and pristine wilderness areas.
- Pacific Crest Trail (PCT): Extending over 2,600 miles from Mexico to Canada, the Pacific Crest Trail passes through the Sierra Nevada, covering a significant portion of the range. Hikers can experience the beauty of the Sierra while trekking along the PCT, exploring varied terrain and ecosystems.
- Rae Lakes Loop: Located in Kings Canyon National Park, the Rae Lakes Loop is a popular backpacking route, approximately 41 miles in length. It showcases stunning alpine lakes, granite cliffs, and picturesque views of the Sierra Nevada high country.
- High Sierra Trail: Beginning in Sequoia National Park, the High Sierra Trail spans around 72 miles, leading hikers through diverse landscapes, including giant sequoias, mountain passes, and concluding at the summit of Mount Whitney.
- Mount Whitney Trail: The Mount Whitney Trail is a challenging but rewarding ascent to the highest peak in the contiguous United States. This trail is around 22 miles round trip and involves steep elevation gains, leading hikers to the summit of Mount Whitney at 14,505 feet.
- Evolution Loop: Located in the Sierra National Forest and Kings Canyon National Park, the Evolution Loop is a remote and scenic trail that covers approximately 56 miles. It showcases stunning vistas, glacially carved valleys, and serene lakes.
- Desolation Wilderness: Offering a variety of trails and numerous alpine lakes, the Desolation Wilderness near Lake Tahoe provides ample opportunities for day hikes and multi-day backpacking adventures. Trails like the Tahoe Rim Trail and various connecting routes offer spectacular views and solitude.
What is the Weather Like in the Sierra Nevada Mountains?
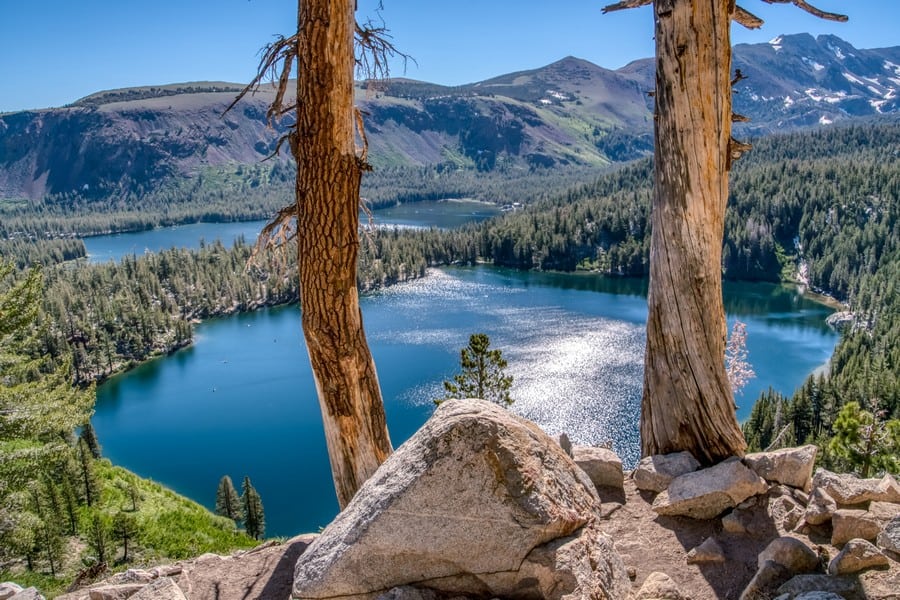

The Sierra Nevada experiences a varied climate due to its diverse topography. Summers are generally warm in lower elevations, while higher elevations enjoy cooler temperatures. Winters bring snowfall to the mountain peaks, attracting skiing enthusiasts and outdoor adventurers.
Here’s an overview of average temperatures in the lower elevations (below 6,000 feet):
- Summer (June to August): Daytime temperatures typically range from 75°F to 90°F (24°C to 32°C) in the lower regions. Nights are cooler, often dropping to around 50°F to 60°F (10°C to 16°C).
- Fall (September to November): Temperatures start to decrease, ranging between 60°F to 80°F (15°C to 27°C) during the day, and nights become colder, averaging between 30°F to 50°F (0°C to 10°C).
- Winter (December to February): In the lower elevations, winter temperatures range from 40°F to 55°F (4°C to 13°C) during the day, dropping to around 20°F to 30°F (-7°C to -1°C) at night. Snowfall is common at higher elevations.
- Spring (March to May): Daytime temperatures increase gradually, ranging from 55°F to 70°F (13°C to 21°C), with nights still quite cool, hovering between 25°F to 40°F (-4°C to 4°C).
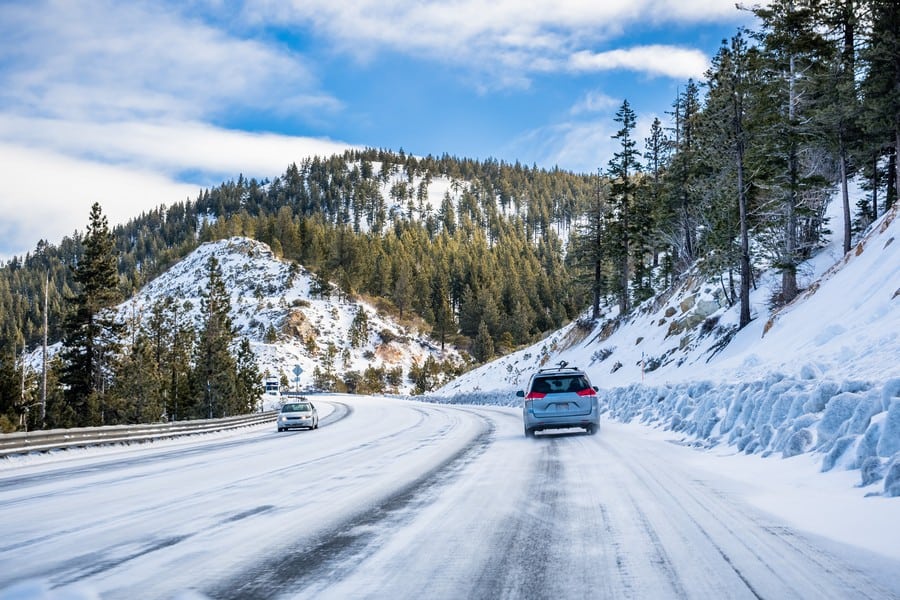

At higher elevations (above 6,000 feet), temperatures can be significantly cooler year-round due to the alpine climate:
- Summer: Daytime temperatures can range from 50°F to 70°F (10°C to 21°C) with cooler nights often dropping to below freezing.
- Winter: Daytime temperatures can vary greatly but generally range from 20°F to 40°F (-7°C to 4°C), and nights are typically well below freezing.
Keep in mind that these temperature ranges are averages, and actual temperatures can fluctuate based on elevation, weather patterns, and specific locations within the Sierra Nevada range.
What Animals Can Be Found in the Sierra Nevada Mountains?
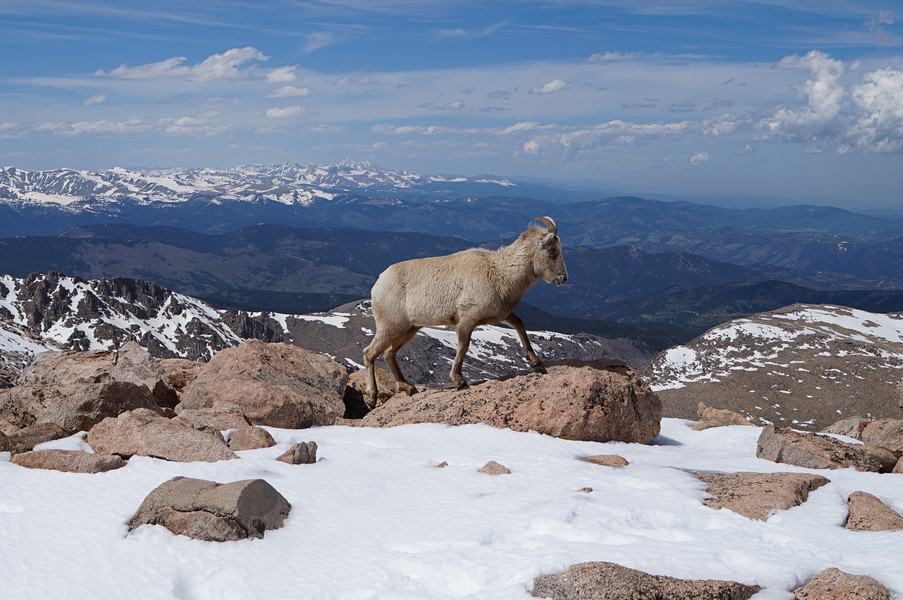

The Sierra Nevada Mountains provide habitat for diverse wildlife, including black bears, mule deer, mountain lions, bighorn sheep, coyotes, bobcats, gray foxes, and various smaller mammals like chipmunks, squirrels, and marmots. There are a variety of bird species such as the peregrine falcon, golden eagle, bald eagle, red-tailed hawk, great horned owl, mountain quail, Steller’s jay, and a variety of songbirds including warblers and finches.
What Plant Life Can Be Found in the Sierra Nevada Mountains?
The Sierra Nevada Mountains host a rich tapestry of plant life. It is known for its coniferous forests that include species like ponderosa pine, Jeffrey pine, sugar pine, incense cedar, white fir, red fir, and various types of spruces. Sequoia trees can only be found in the Sierra Nevada mountains. There are an estimated 80,000 still alive.
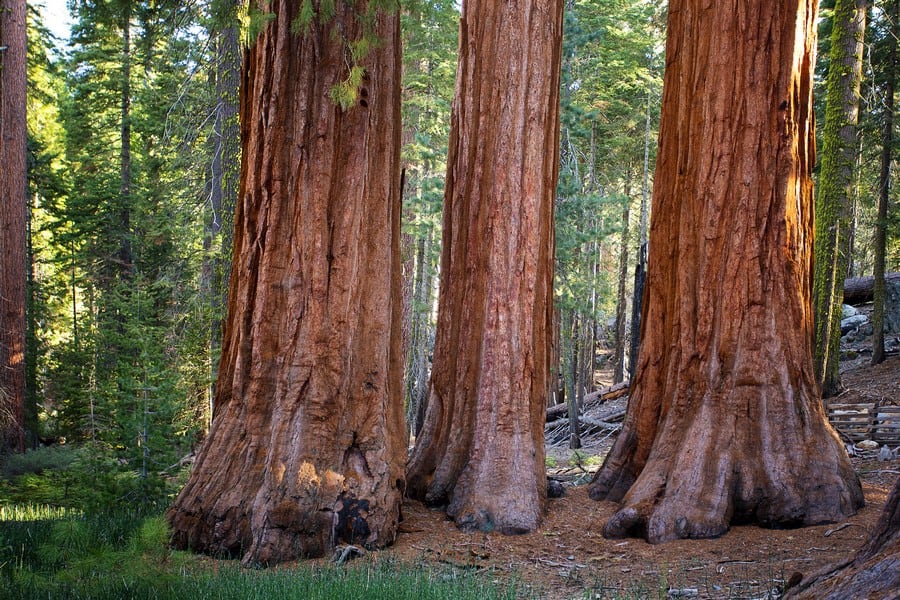

Quaking aspen and cottonwood trees are among the deciduous trees found at lower elevations. Its alpine meadows adorned with vibrant wildflowers particularly during spring and summer, including lupines, Indian paintbrush, mariposa lilies, corn lilies, and mountain dandelions.
Who Lived in the Sierra Nevada Mountains?
The Sierra Nevada was inhabited by various indigenous groups for thousands of years before they were displaced by European settlers. Some of the indigenous peoples that lived in the Sierra Nevada area include the:
- Miwok: The Miwok people were among the primary Native American groups in the central Sierra Nevada. They resided in the western foothills and the central valley areas.
- Washoe: The Washoe people lived around the eastern Sierra Nevada and the Lake Tahoe region, covering parts of present-day California and Nevada.
- Paiute: The Northern Paiute people inhabited areas to the east of the Sierra Nevada in the Great Basin region. While not primarily located in the Sierra Nevada, their territory included regions close to the eastern slopes.
- Shoshone: Some Shoshone groups resided in the eastern foothills of the Sierra Nevada.