The following information was obtained from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Tanzania.
Recommended Vaccinations and Preventive Medications
The following vaccines may be recommended for your travel to East Africa. Discuss your travel plans and personal health with a health-care provider to determine which vaccines you will need.
- Hepatitis A or immune globulin (IG). Transmission of hepatitis A virus can occur through direct person-to-person contact; through exposure to contaminated water, ice, or shellfish harvested in contaminated water; or from fruits, vegetables, or other foods that are eaten uncooked and that were contaminated during harvesting or subsequent handling.
- Hepatitis B, especially if you might be exposed to blood or body fluids (for example, health-care workers), have sexual contact with the local population, or be exposed through medical treatment. Hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for all infants and for children ages 11-12 years who did not receive the series as infants.
- Malaria: your risk of malaria may be high in all countries in East Africa, including cities. See your health care provider for a prescription antimalarial drug.
- Meningococcal (meningitis) if you plan to visit countries in this region that experience epidemics of meningococcal disease during December through June.
- Rabies, pre-exposure vaccination, if you might have extensive unprotected outdoor exposure in rural areas, such as might occur during camping, hiking, or bicycling, or engaging in certain occupational activities.
- Typhoid vaccine. Typhoid fever can be contracted through contaminated drinking water or food, or by eating food or drinking beverages that have been handled by a person who is infected. Large outbreaks are most often related to fecal contamination of water supplies or foods sold by street vendors
- Yellow fever, a viral disease that occurs primarily in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America, is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The virus is also present in Panama and Trinidad and Tobago. Yellow fever vaccination is recommended for travelers to endemic areas and may be required to cross certain international borders (For country specific requirements, see Yellow Fever Vaccine Requirements and Information on Malaria Risk and Prophylaxis, by Country.). Vaccination should be given 10 days before travel and at 10 year intervals if there is on-going risk.
- As needed, booster doses for tetanus-diphtheria, measles, and a one-time dose of polio vaccine for adults.
Malaria
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. Humans get malaria from the bite of a mosquito infected with the parasite. Your risk of malaria may be high in all countries in East Africa, including cities. All travelers to East Africa, including infants, children, and former residents of East Africa, may be at risk for malaria. Prevent this serious disease by seeing your health care provider for a prescription antimalarial drug and by protecting yourself against mosquito bites.
All travelers should take one of the following drugs:
- atovaquone/proguanil,
- doxycycline,
- mefloquine, or
- primaquine (in special circumstances).
Yellow Fever
A certificate of yellow fever vaccination is required for entry into Tanzania when arriving from countries where yellow fever is present.
Food and Waterborne Diseases
Make sure your food and drinking water are safe. Food and waterborne diseases are the primary cause of illness in travelers. Travelers’ diarrhea can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites, which are found throughout East Africa and can contaminate food or water. Infections may cause diarrhea and vomiting (E. coli, Salmonella, cholera, and parasites), fever (typhoid fever and toxoplasmosis), or liver damage (hepatitis).
Covid
As of September 15, 2022, travelers arriving to Tanzania by air are now exempt from all vaccination and testing requirements. Therefore, there are no Covid-19 related requirements for nearly all of our clients, who fly in and out of Kilimanjaro airport for their trips.

However, for those coming to Tanzania through land borders (such as crossing over from Kenya), there are still requirements for vaccinated and unvaccinated travelers.
Fully vaccinated travelers (those with two doses of vaccines) arriving through land borders are exempt from COVID-19 test requirements for entry to Tanzania, provided that they present a valid vaccination certificate for verification.
Unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated travelers arriving through land borders are required to present a negative Covid-19 test to enter Tanzania. The test must be a PCR Test that was done within 72 hours of departure to Tanzania. Travelers who are not fully vaccinated may also be required to take a Rapid Antigen Test upon arrival through land borders. We are not responsible for clients who are denied entry due to failure to meet Tanzania’s regulations.
Ebola
You have probably heard the news about the periodic Ebola outbreaks in Africa. In 2014-2015, there were 28,616 reported cases originating in West Africa (Sierra Leone, Guinea, Liberia).
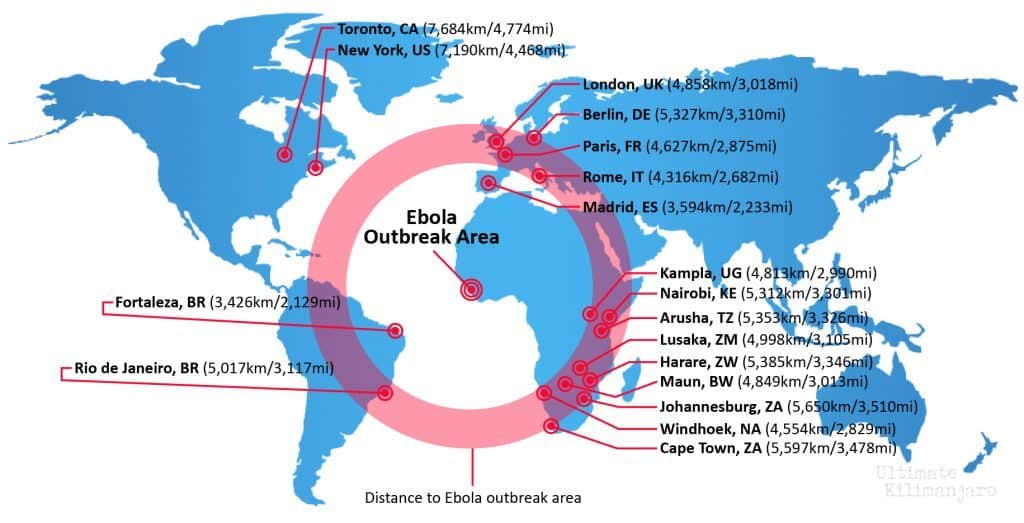
There is currently zero risk of exposure to Ebola while in Tanzania. As the map illustrates, the outbreak was many thousands of miles away and many years ago. Ebola is transmitted through direct contact with an infected person’s body fluids. Infected people are not contagious during the incubation period, and only become contagious with the onset of symptoms. Therefore people who are most at risk are health care workers and families of infected people, not tourists.
Learn more about Ebola here.