The United States has more than 200 mountain ranges, varying widely in size, elevation, and geological composition. They were formed through various geological processes over millions of years.
How Were US Mountain Ranges Formed?
Mountain ranges are formed through tectonic plate movements, volcanic activity, and erosion.
Tectonic plates are massive pieces of the Earth’s crust. When they collide, they can create fold mountains, where layers of rock are pushed upwards to form peaks and ridges. The Rocky Mountains are an example of fold mountains that were made through the collision and uplift of the North American and Pacific plates. Faulting, or the cracking and shifting of the Earth’s crust, has also contributed to the formation of ranges such as the Sierra Nevada.

Volcanic activity is another way mountain ranges are formed. When tectonic plates move towards each other, one plate can be pushed deeper into the Earth, where it melts and forms magma. Tectonic plates can also move away from each other, creating a gap that allows magma to rise to the surface. Through repeated volcanic eruptions, mountains are built up layer by layer. For instance, the Cascade Range is a result of volcanic activity.
Lastly, mountains can be shaped by erosion. The Appalachian Mountains, for example, are some of the oldest mountains on Earth and have been heavily eroded by glacial activity over millions of years.

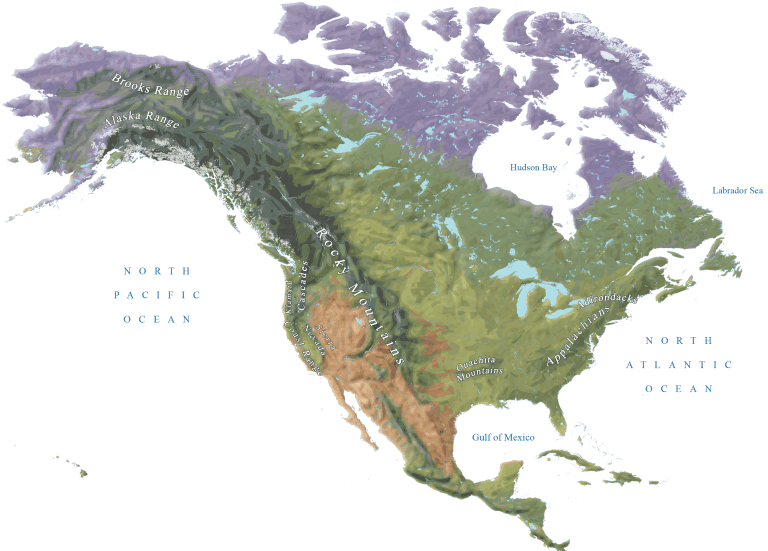
Major Mountain Ranges of the USA
Here are the most notable mountain ranges in the USA:
- Appalachian Mountains
- Rocky Mountains
- Sierra Nevada
- Alaska Range
- Cascade Range
- Brooks Range
- Adirondack Mountains
- Coast Range
- Klamath Mountains
- Ouachita Mountains
1. Appalachian Mountains

The Appalachian Mountains stretch from Newfoundland in Canada to Alabama, spanning over 2,000 miles (3,200 km). They are among the oldest mountains on Earth, estimated to be over 480 million years old. Their rounded and smooth appearance is due to millennia of erosion. This range has been the backdrop for many historical events, from early frontier days to the Civil War. The Great Smoky Mountains National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage site.
2. Rocky Mountains

The Rocky Mountains extend over 3,000 miles (4,828 km) from British Columbia in Canada to New Mexico in the USA. Known for their rugged terrain and towering peaks, they include famous summits like Colorado’s Pikes Peak and Longs Peak. The Rockies were a barrier for westward expansion in the 19th century, shaping historical events such as the quest for gold and the construction of the First Transcontinental Railroad. Home to national parks like Rocky Mountain and Yellowstone, the Rockies are a sanctuary for diverse wildlife, including grizzly bears and elk.
3. Sierra Nevada

The Sierra Nevada, primarily in California and extending into Nevada, spans about 400 miles (644 km). It features famous mountains such as Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the contiguous United States at 14,505 feet (4,421 m), and the beautiful Yosemite Valley. This range was the epicenter of the California Gold Rush in 1849, which forever changed American history. The Sierra Nevada is a favorite among hikers, skiers, and climbers.
4. Alaska Range

The Alaska Range is a 600-mile (965 km) crescent-shaped chain in Central Alaska. Dominated by Denali, North America’s tallest peak at 20,310 feet (6,190 m), this range offers a challenging environment for mountaineers. Beyond its heights, the Alaska Range features sweeping glaciers and vast wilderness areas. Grizzly bears and moose roam this habitat. Denali National Park is a key attraction, offering jaw-dropping views and unique wildlife experiences.
5. Cascade Range

The Cascade Range is a prominent mountain range in western North America. It stretches approximately 700 miles (1,127 km) from north to south, forming a major portion of the Pacific Ring of Fire. This range is characterized by its series of volcanic peaks including Mount Rainier and Mount St. Helens. Several national parks and forests are located within the Cascade Range, providing protections for its natural resources and recreational opportunities for visitors. Notable parks include Mount Rainier National Park, North Cascades National Park, and Crater Lake National Park.
6. Brooks Range

The Brooks Range is one of the most remote and pristine mountain ranges in North America. It stretches approximately 720 miles (1,158 km) from west to east across northern Alaska and into Canada’s Yukon Territory. The Brooks Range is situated entirely above the Arctic Circle, making it one of the northernmost mountain ranges in the world. It acts as a natural divide between the Arctic coastal plain to the north and the tundra to the south. The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge is home to polar bears, caribou, and musk oxen.
7. Adirondack Mountains

Located in New York, the Adirondack Mountains comprise 46 high peaks, with Mount Marcy being the tallest at 5,344 feet (1,629 m). The Adirondack Park, established in 1892, covers approximately 6 million acres (2.4 million hectares), making it the largest publicly protected area in the contiguous United States. It supports wildlife such as black bears, moose, white-tailed deer, and bobcats. The name “Adirondack” comes from a Mohawk word meaning “bark eaters.”
8. Coast Range

The Pacific Coast Range consists of several smaller subranges, including the Olympic Mountains in Washington, the Oregon Coast Range, and the California Coast Ranges. These mountains are positioned parallel to the Cascades, stretching north to south from Alaska to California. The Coast Range is geologically young compared to the Rockies and the Appalachians. The redwood forests in Northern California are a highlight. These ancient trees, some over 2,000 years old, are some of the tallest trees in the world.
9. Klamath Mountains

The Klamath Mountains comprise a rugged mountain range that spans parts of northern California and southern Oregon. The mountains cover approximately 15,000 square miles (38,850 km²) and include several subranges, such as the Trinity Alps, Marble Mountains, and Siskiyou Mountains. The highest peak in the Klamath Mountains is Mount Eddy, which rises to 9,025 feet (2,751 m). The discovery of gold in the mid-19th century brought an influx of miners and settlers to the area.
10. Ouachita Mountains

The Ouachita Mountains are located in south-central United States, in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahama. Unlike most North American mountain ranges that run north-south, the Ouachitas have a distinct east-west alignment, stretching approximately 225 miles (362 km). Magazine Mountain, the highest peak, stands at 2,800 feet (853 m). The Ouachitas were historically inhabited by Native American tribes and its name is derived from Native American languages.